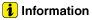Kia Niro: Cylinder Head Assembly / Cylinder Head Repair procedures
| Removal |
Engine removal is not required for this procedure.
|
|
Mark all wiring and hoses to avoid misconnection. |
| 1. |
Shut off the High Voltage circuit. (Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "High Voltage Shutoff Procedure") |
| 2. |
Remove the air cleaner assembly. (Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Air Cleaner") |
| 3. |
Remove the engine room under cover. (Refer to Engine and Transaxle Assembly - "Engine Room Under Cover") |
| 4. |
Drain the engine coolant. (Refer to Cooling System - "Coolant") |
| 5. |
Drain the inverter coolant. (Refer to Hybrid Motor System - "Coolant") |
| 6. |
Disconnect the radiator upper hose (A).
|
| 7. |
Disconnect the radiator lower hose (A).
|
| 8. |
Remove the hybrid power control unit (HPCU) and tray. (Refer to Hybrid Control System - "Hybrid Power Control Unit (HPCU)") |
| 9. |
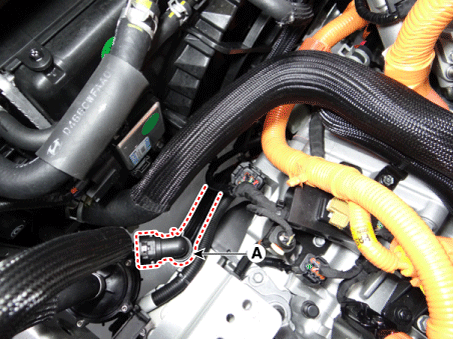
Disconnect the reservoir tank coolant hose (A).
|
| 10. |
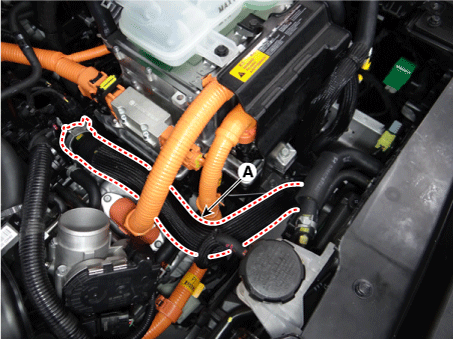
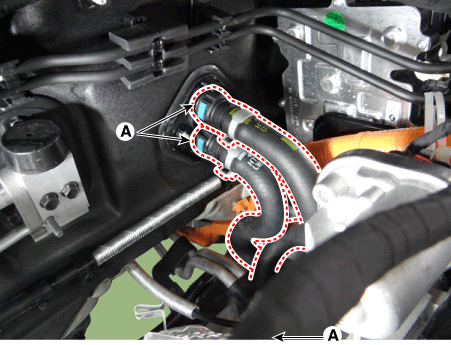
Disconnect the hybrid starter generator (HSG) coolant hose (A).
|
| 11. |
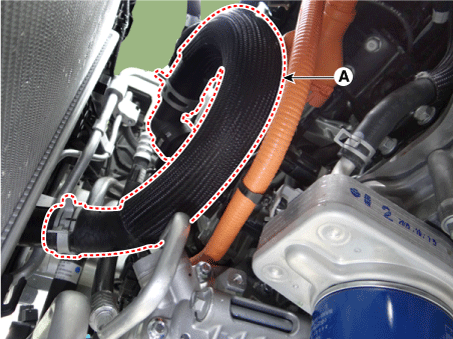
Disconnect the electric water pump (EWP) coolant hose (A).
|
| 12. |
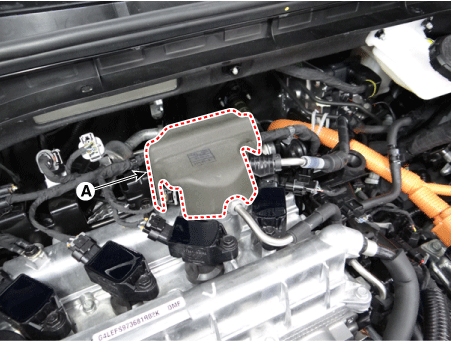
Remove the high pressure fuel pump foam (A).
|
| 13. |
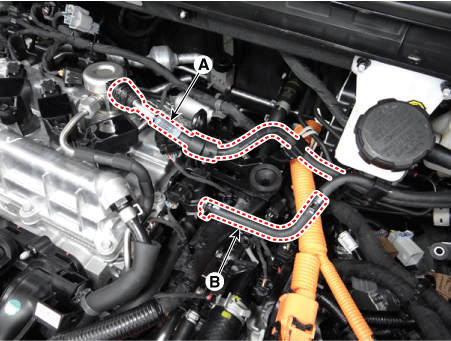
Disconnect the fuel hose (A) and purge control solenoid valve (PCSV) hose (B).
|
| 14. |
Disconnect the heater hose (A).
|
| 15. |
Remove the front muffler. (Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Muffler") |
| 16. |
Remove the water temperature control assembly and heater pipe. (Refer to Cooling System - "Water Temperature Control Assembly") |
| 17. |
Remove the intake manifold. (Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Intake Manifold") |
| 18. |
Remove the hybrid starter generator (HSG). (Refer to Hybrid Motor System - "Hybrid Starter Generator (HSG)") |
| 19. |
Remove the electric EGR control valve. (Refer to Engine Control/Fuel System - "Electric EGR Control Valve") |
| 20. |
Remove the spark plugs. (Refer to Engine Electrical System - "Spark Plug") |
| 21. |
Remove the cylinder head cover. (Refer to Cylinder Head Assembly - "Cylinder Head Cover") |
| 22. |
Remove the exhaust manifold. (Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Exhaust Manifold") |
| 23. |
Remove the timing chain. (Refer to Timing System - "Timing Chain") |
| 24. |
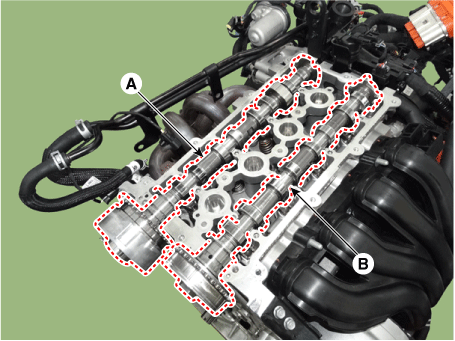
Remove the CVVT & camshaft.
|
| 25. |
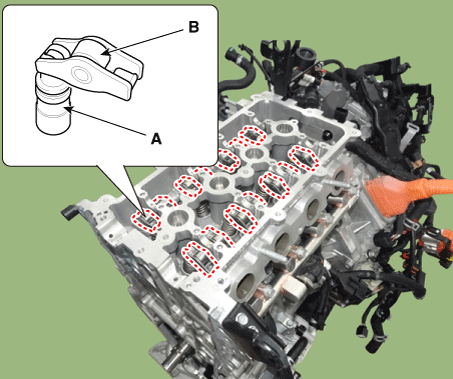
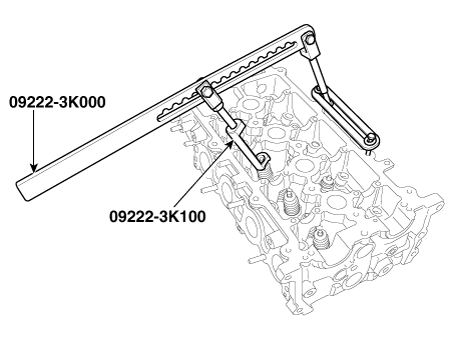
Remove the hydraulic lash adjuster (HLA) (A) and the swing arm (B).
|
| 26. |
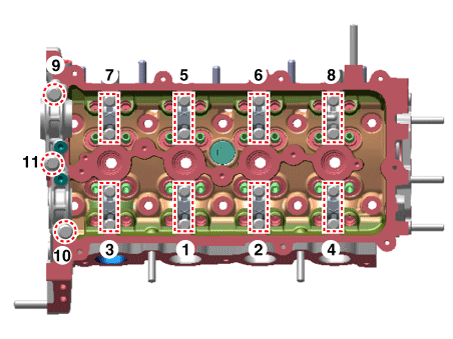
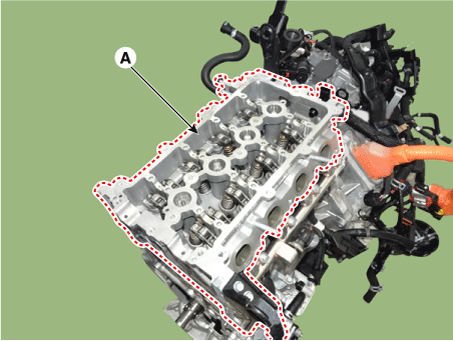
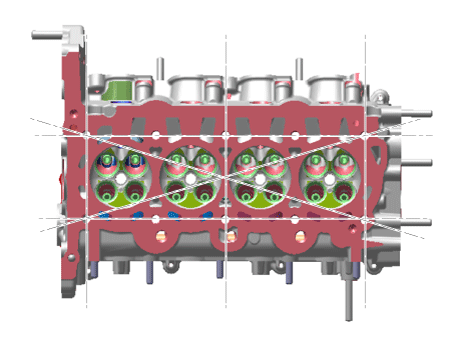
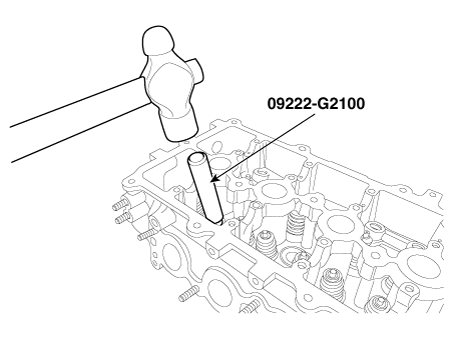
Remove the cylinder head.
|
| Disassembly |
Identify valves and valve springs as they are removed so that each item can be reinstalled in its original position. |
| 1. |
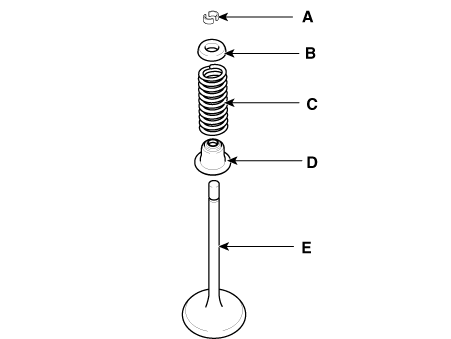
Remove the valves.
|
| Inspection |
Cylinder Head
| 1. |
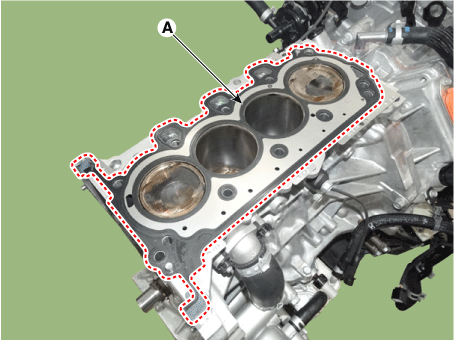
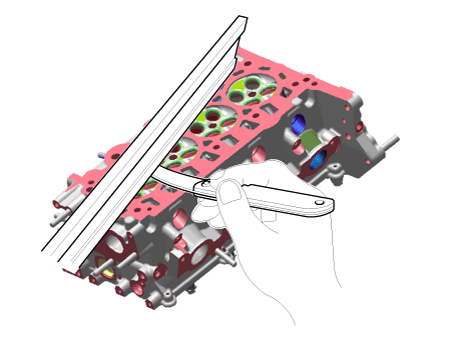
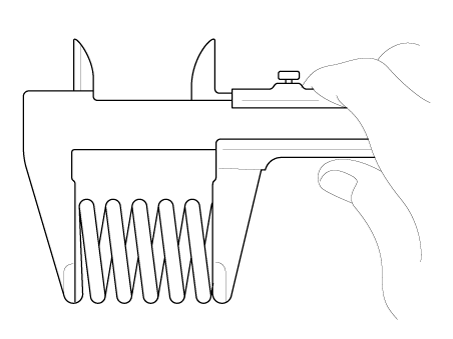
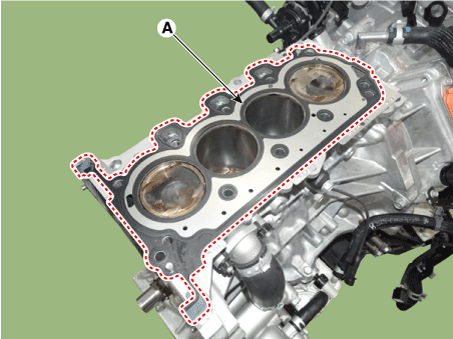
Inspect for flatness.
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the contacting surface of the cylinder block and check the manifolds for warpage.
|
| 2. |
Inspect for cracks. Check the combustion chamber, intake ports, exhaust ports and cylinder block surface for cracks. If cracked, replace the cylinder head. |
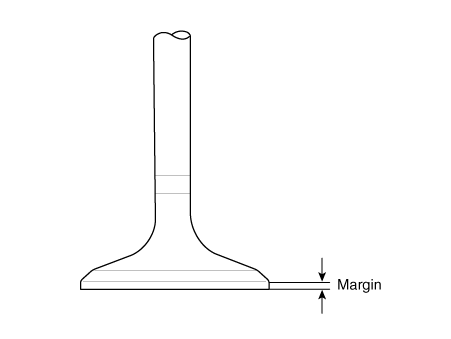
Valve And Valve Spring
| 1. |
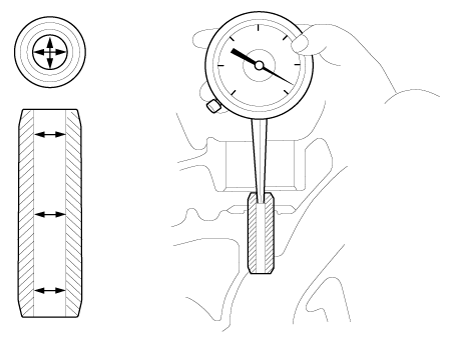
Inspect valve stems and valve guides.
|
| 2. |
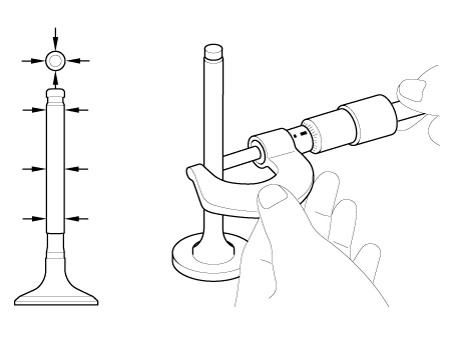
Inspect the valves.
|
| 3. |
Inspect the valve seats and the valve guides.
|
| 4. |
Inspect the valve springs
|
HLA (Hydraulic Lash Adjuster)
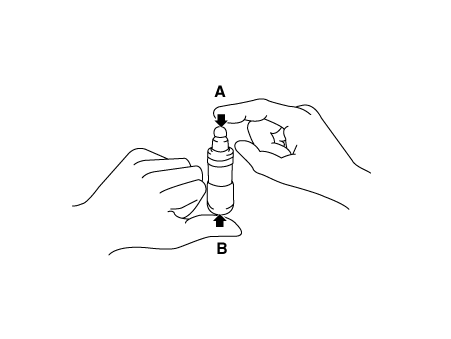
With the HLA filled with engine oil, hold A and press B by hand.
If B moves, replace the HLA.
|
Problem |
Possible cause |
Action |
||||
|
1. Temporary noise when starting a cold engine |
Normal |
This noise will disappear after the oil in the engine reaches the normal
pressure. |
||||
|
2. Continuous noise when starting the engine after being parked for more
than 48 hours |
Oil leakage of the high pressure chamber on the HLA, allowing air to get
in |
Noise will disappear within 15 minutes when engine runs at 2000-3000 rpm.
If it doesn’t disappear, refer to step 7 below. |
||||
|
3. Continuous noise when the engine is first started after rebuilding cylinder
head |
Insufficient oil in cylinder head oil gallery |
|||||
|
4. Continuous noise when the engine is started after excessively cranking
the engine by the starter motor or band |
|
|||||
|
5. Continuous noise when the engine is running after changing the HLA
|
|
|||||
|
6. Continuous noise during idle after high engine speed |
Engine oil level too high or too low |
|
||||
|
Excessive amount of air in the oil at high engine speed |
Check oil supply system. |
|||||
|
Deteriorated oil |
Check oil quality. If deteriorated, replace with specified type. |
|||||
|
7. Noise continues for more than 15 minutes |
Low oil pressure |
Check oil pressure and oil supply system of each part of engine. |
||||
|
Faulty HLA |
Remove the cylinder head cover and press HLA down by hand. If it moves, replace the HLA. |
| Reassembly |
|
| 1. |
Install the valves.
|
| Installation |
|
| 1. |
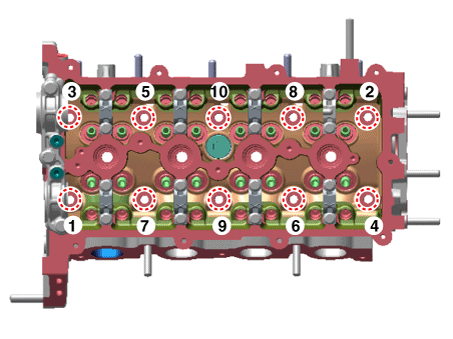
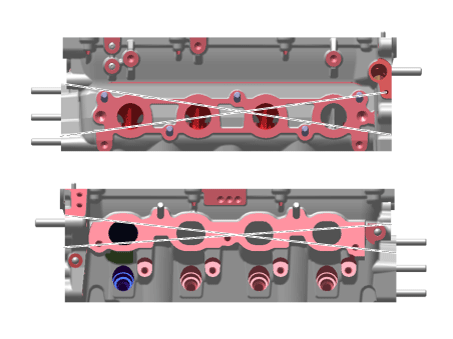
Install the cylinder head gasket on the cylinder block.
|
| 2. |
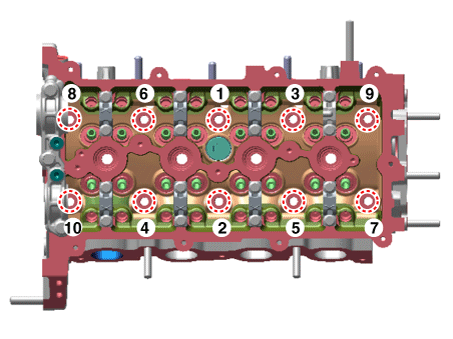
Install the cylinder head assembly.
|
| 3. |
Install the hydraulic lash adjuster (HLA) (A) and the swing arm (B).
|
| 4. |
Install the remaining parts in the reverse order of removal. |
| 5. |
Add all the necessary fluids and check for leaks. Connect KDS/GDS. Check for codes, note, and clear. Recheck.
|
 CVVT & Camshaft Repair procedures
CVVT & Camshaft Repair procedures
Removal
•
Use fender covers to avoid damaging painted surfaces.
...
Other information:
Kia Niro 2017 (DE HEV) Service Manual: Compressor Description and operation
Description
Electric compressor improves the fuel efficiency and operates the air conditioner
even when the engine is stopped.
Operation Principle
Compression Part
One of the scrolls is fixed while the other orbits eccentrically without self-rotating,
thereby to trap ...
Kia Niro 2017 (DE HEV) Service Manual: General information
Document Purpose
The purpose of this document is to familiarize first responders and the towing/roadside
assistance industry with the proper methods to handle the Niro in an emergency situation.
This guide gives a basic overview of key vehicle systems and instructions for dealing
with the dif ...